Welcome to our latest blog post on “The Bankers Laddar,” your trusted source for cracking the JAIIB exams. Today, we delve deep into the concept of inflation, focusing on how it’s measured and the critical role of the price index in understanding economic shifts. Whether you are revisiting these concepts or encountering them for the first time, this post will provide you with a clear understanding of inflation metrics.
What is Inflation and How is it Measured?
Inflation indicates the rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services rises, subsequently eroding purchasing power. The primary tool for measuring inflation is the price index, which tracks the price changes of a selected basket of goods and services over time.
Defining the Price Index
A price index represents the weighted average prices of a selected basket of goods and services in comparison to their prices during a base year. This index is crucial for calculating inflation as it reflects changes in price levels that consumers face.
Calculating the Weighted Average
To understand how a price index is computed, consider a simple example:
-
Commodity A: ₹20, 80 units consumed
-
Commodity B: ₹18, 100 units consumed
-
Commodity C: ₹22, 200 units consumed
The price index uses a weighted average where more frequently consumed commodities hold greater significance. Thus, the formula involves multiplying each commodity’s price by its consumption units, summing these products, and then dividing by the total number of units consumed.
The Role of the Base Year in Price Indexes
Every price index selects a base year, with its index value usually set at 100. This base year serves as a benchmark to compare current prices and determine inflation rates.
Calculating Inflation Using Price Indexes
To calculate inflation, take the price index of the current period, subtract the price index from the previous year, and then divide by the previous year’s index. Multiply the result by 100 to get the percentage rate of inflation.
For instance:
-
Price Index in April 2023: 173.70
-
Price Index in April 2022: 169.30
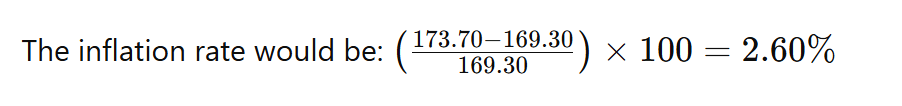
Understanding how to calculate and interpret the price index and inflation rates is crucial for economic literacy, especially for banking professionals preparing for the JAIIB exams. We hope this post clarifies these economic indicators and aids your study preparations.
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to helping you succeed in your JAIIB examination. Stay tuned for more insightful posts!
